Abstract
Introduction MF is a clonal myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) characterized by activated JAK-STAT signaling, bone marrow (BM) fibrosis, anemia, organomegaly, a variety of symptoms and shortened survival. Ruxolitinib (rux) is a JAK1/2 inhibitor that reduces splenomegaly and improves symptoms of MF, but has little effect on BM fibrosis or the JAK2V617F allele burden, creating a need for ruxolitinib-based disease-modifying drug combinations. Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACis) have pleiotropic effects in neoplastic cells via acetylation of histone and non-histone proteins. In particular, HDACis down-regulate JAK2 through acetylation and disruption of the chaperone function of heat shock protein 90. Pracinostat is an oral HDACi with modest single agent efficacy in MF (Quintas-Cardama, Leuk Res 2012). We tested the combination of rux and pracinostat in this phase 2 trial (NCT02267278).
Methods Newly diagnosed or previously treated adults with primary MF (PMF), post-polycythemia vera MF (PPV-MF) or post-essential thrombocythemia MF (PET-MF) with palpable splenomegaly ≥5 cm, neutrophils ≥1 x 109/L and platelets ≥50 x109/L were eligible. Newly diagnosed pts had to be intermediate or high risk by the IPSS. Prior JAK inhibitor therapy was not allowed, except for rux of <3 months' duration and ongoing. Cycles were 4 weeks long. Rux was administered alone for the first 3 cycles, dosed per label. Pracinostat was added in cycle 4 at a dose of 60 mg 3 times weekly during the first 3 weeks. Response assessment was per IWG-MRT 2013 criteria. BM examination was required after cycles 6 and 12. Spleen and liver size were measured by palpation. The MPN-SAF TSS questionnaire was administered every cycle for the first 7 cycles and then every 3 cycles.
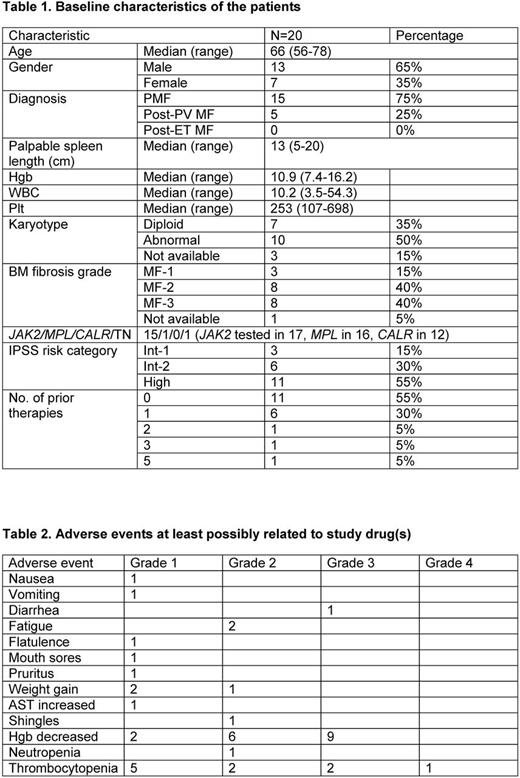
Results 25 pts were enrolled. 5 never received pracinostat (1 proceeded to SCT, 1 transformed to AML, 2 had new cancer diagnoses, 1 was on a prohibited concurrent medication) and are not considered further. Baseline characteristics of the 20 pts who received both drugs are presented in Table 1. Five pts remain on study. Reasons for discontinuation in the other 15 were: anemia/increased RBC transfusion requirements (4), logistical/financial constraints (4), anemia and myocardial infarction on study (1), thrombocytopenia/pt request (1), MF progression (2), transformation to AML (1), recurrence of skin cancer requiring therapy (1), and SCT (1). The median number of cycles of study drugs received is 11 (3-32), although pracinostat is currently on hold in 2 pts on study (anemia (1), thrombocytopenia (1)) and was on hold in 9 pts before discontinuation from the study (grade 2 fatigue/diarrhea (1), anemia/increased RBC transfusion requirements (3), thrombocytopenia (1), both anemia and thrombocytopenia (1), QTc prolongation unrelated to pracinostat (1), concomitant therapy with sertraline (1), allergic-type reaction (1)). The median time on pracinostat was 7.8 (0-26.3) months. Pracinostat dose reduction from 60 to 45 mg occurred in 1 pt currently on study and 6 pts now off study. A best response of clinical improvement (CI) in splenomegaly (n=4), symptoms (n=2) or both (n=10) occurred in 16 pts; 3 had stable disease and 1 progressive disease. The median time to and duration of response were 1.6 (0.9-15.9) and 7.5 (3-23.5) months, respectively. There were no anemia or cytogenetic responses. One pt had a decrease in his BM mutated JAK2 allele burden from 65% to 0.27% after 27 cycles of therapy, coincident with a decrease in BM fibrosis grade (MF-3 to MF-1) over 25 months. BM fibrosis improved from MF-3 to MF-2 over 5.5 months in another pt. Adverse events possibly attributable to the study drugs are listed in Table 2. Updated results will be presented at the meeting.
Conclusions In this study, the addition of pracinostat to ruxolitinib in pts with MF yielded modest clinical benefits over those expected with rux alone. Anemia and thrombocytopenia were frequent, sometimes leading to discontinuation of pracinostat. Disease-modifying benefits of the combination may emerge late, as evidenced by the achievement of a near-complete molecular remission and reduction in BM fibrosis by 2 grades in 1 pt.
Bose: Incyte Corporation: Honoraria. Pemmaraju: Incyte: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Stemline: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Cellectis: Research Funding; LFB: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Jabbour: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy. Daver: Sunesis Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kiromic: Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo: Research Funding; Jazz: Consultancy; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy; Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc.: Consultancy; Pfizer Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Incyte Corporation: Honoraria, Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Research Funding; Immunogen: Research Funding. DiNardo: Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Agios: Honoraria, Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo: Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding. Kantarjian: Pfizer: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Delta-Fly Pharma: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Bristol-Meyers Squibb: Research Funding; ARIAD: Research Funding. Verstovsek: Incyte: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Blueprint Medicines Corp: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Galena BioPharma: Research Funding; Blueprint Medicines Corp: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; CTI BioPharma Corp: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Lilly Oncology: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Astrazeneca: Research Funding; Astrazeneca: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding; Galena BioPharma: Research Funding; CTI BioPharma Corp: Research Funding; Lilly Oncology: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.